Abstract:
Mastering the 4 C's A Guide to Understanding Wine
Wine is a complex and fascinating beverage that is enjoyed by people all over the world. The process of understanding wine can be overwhelming, with so many variables to consider. However, by mastering the 4 C's - Color, Clarity, Aroma, and Taste - wine enthusiasts can gain a deeper appreciation and understanding of this incredible drink. This article will delve into each of the 4 C's, providing detailed explanations and insights to help readers enhance their knowledge of wine appreciation.

1. Color:
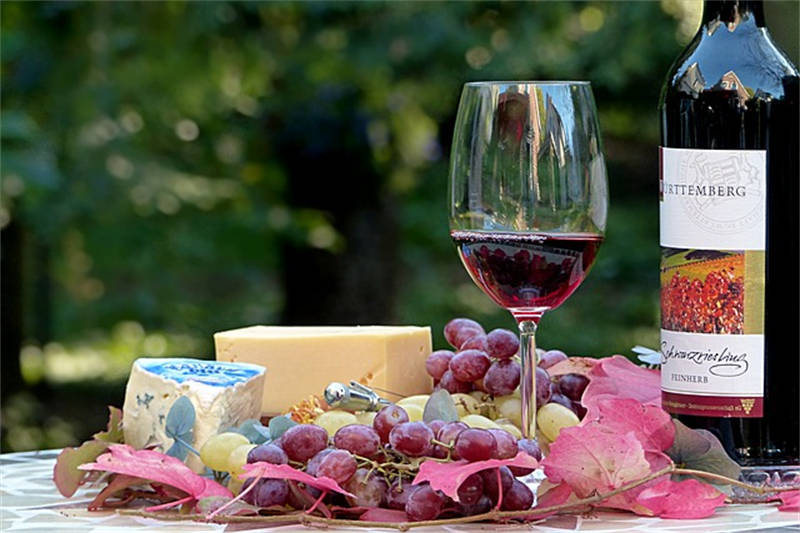
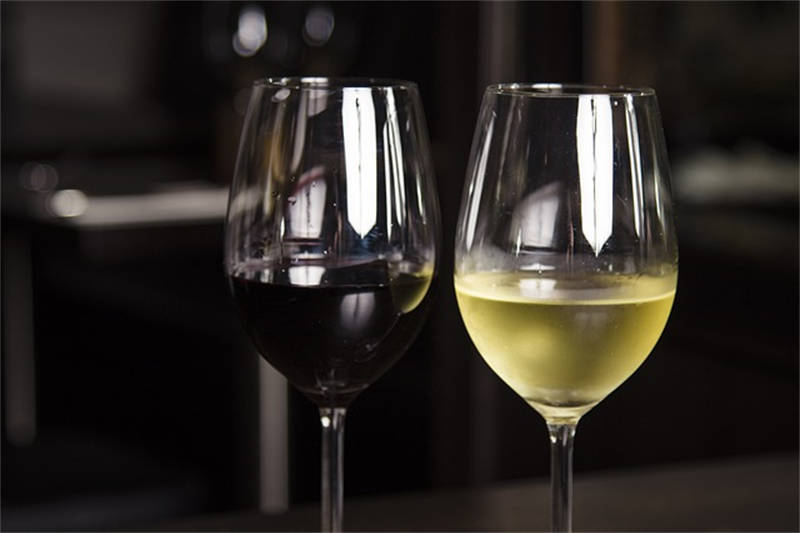
The color of wine serves as an initial indicator of its age, quality, and grape variety. When examining the color of wine, it is essential to consider both the hue and intensity. The hue refers to the shade of the color, ranging from pale yellow to dark purple, while the intensity reflects the depth and saturation of the color. For example, a vibrant ruby red color may indicate a young and fruity red wine, while a golden hue often signifies an older white wine.
Moreover, the color of wine can also provide insights into the winemaking process. For instance, white wines tend to have lighter colors due to minimal contact with grape skins during fermentation, while red wines acquire their color from prolonged skin contact. By observing wine's color, enthusiasts can start to discern the characteristics and potential flavor profiles of different wines.
2. Clarity:
The clarity of wine refers to its transparency and freedom from unwanted particles, such as sediments, cloudiness, or impurities. While slight haziness can be acceptable in certain styles, clear wines are generally preferred. Achieving clarity in wine is the result of careful handling during production and proper filtration techniques.
Apart from aesthetics, clarity can also indicate the wine's age and quality. Younger wines are more likely to have sediments and may require decanting or careful pouring to separate the wine from any solids. On the other hand, older wines often develop sediments over time, indicating their maturity. By evaluating the clarity of the wine, enthusiasts can assess its quality and assess the potential need for further steps in the serving process.
3. Aroma:
Aroma plays a crucial role in wine appreciation, as it contributes immensely to the overall sensory experience. The aromatic compounds in wine originate from the grapes themselves, predominantly from their skins, as well as the fermentation process and aging in oak barrels. The different grape varieties, growing regions, and winemaking practices all influence the aroma of the wine.
There is a wide range of aromas in wine, including fruity, floral, earthy, and spicy notes. When examining the aroma, it is helpful to swirl the wine gently in the glass to release its fragrance. By exploring the various scents present, such as blackberries, vanilla, or violets, enthusiasts can develop a better understanding of the grape variety, region, and potential flavor profile of the wine.
4. Taste:
Taste is the final and most crucial aspect of understanding wine. While the 4 C's discussed so far provide valuable insights, ultimately, it is the taste that determines a person's preference for a particular wine. The taste of wine encompasses several elements, including sweetness, acidity, tannins, and body.
Sweetness refers to the perception of sugar in the wine and can range from bone dry to lusciously sweet. Acidity contributes to the wine's freshness and can range from low to high levels, providing a crisp or zesty character. Tannins are compounds found mainly in red wines, contributing to their structure and mouth-drying sensation. Lastly, body refers to the weight and tactile sensation of the wine in the mouth, ranging from light-bodied to full-bodied.
Mastering the taste of wine requires practice and experimentation. By comparing and contrasting different wines, enthusiasts can refine their palate and gain a deeper appreciation for the subtleties and complexities of wine.
Conclusion:
Mastering the 4 C's - Color, Clarity, Aroma, and Taste - has a profound impact on understanding wine. By paying attention to the color, enthusiasts can gather essential information about age and variety. Clarity indicates the wine's quality and potential need for additional steps. Aroma unravels the wine's story and characteristics, while taste is the ultimate judge of preference. By immersing oneself in the world of wine and embracing these 4 C's, individuals can enhance their wine appreciation and embark on an enriching journey of exploration and discovery.